TPS: the OIC Trade Preferential System
WE HELP YOU DOING BUSINESS: by providing Trade agreements, Concessions, Procedures and more, are all available to help you doing business across OIC countries.
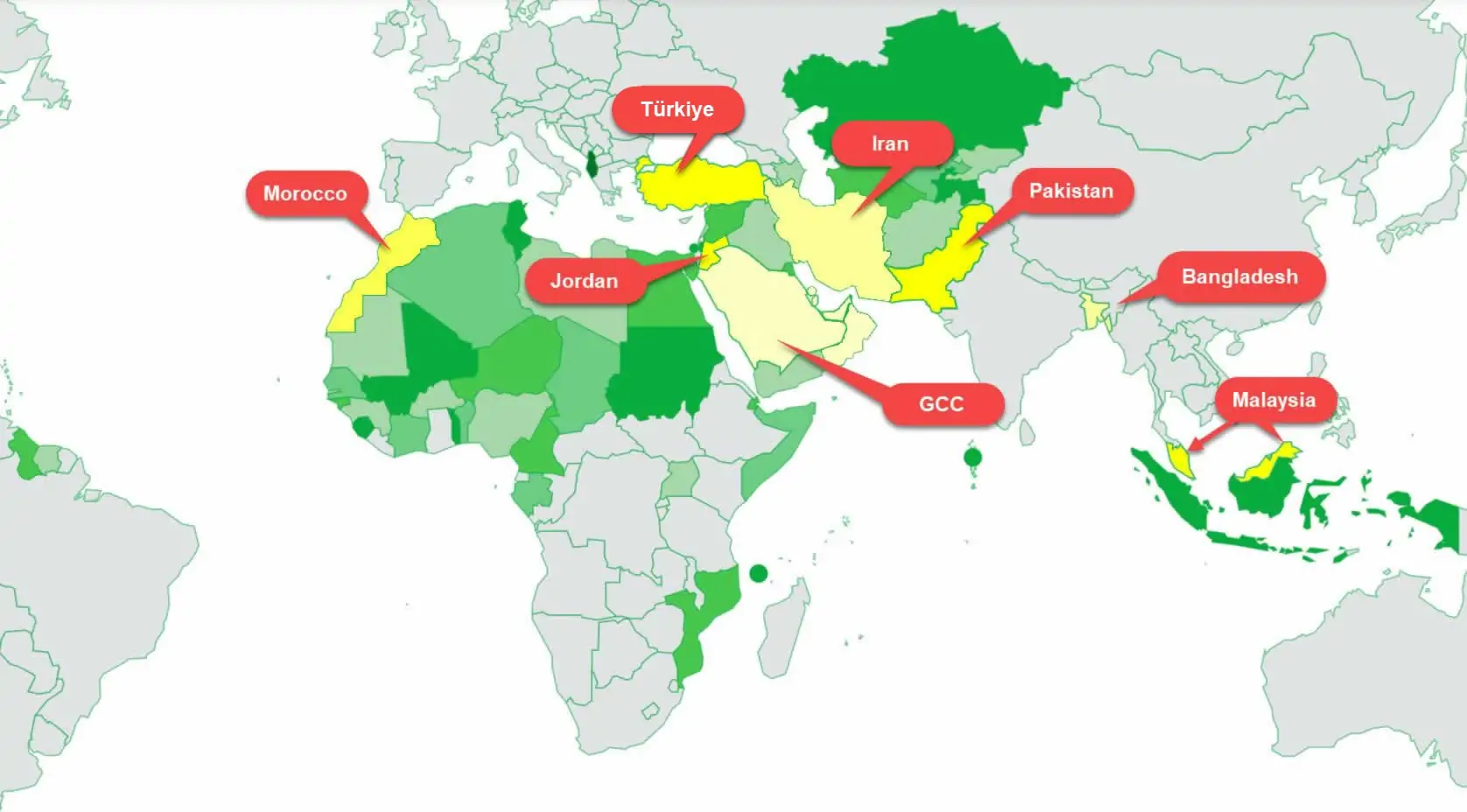
Current signatory Countries
Frequently Asked Questions
1- What is TPS-OIC ?
TPS-OIC is one of the projects of COMCEC. The objective of the TPS-OIC is to promote the intra-OIC trade through exchange of trade preferences among the Member States.
2- What is the Framework Agreement on TPS-OIC ?
The Framework Agreement on TPS-OIC is the basic legal document of the TPS-OIC, which sets up the general principles towards establishing a preferential system, such as the general rules of the negotiations and the scope of goods coverage etc. The Agreement entered into force in the autumn of 2002, after 10 OIC Member States had ratified it.
Among the main features of the Agreement are the Most Favored Nation principle, equal treatment of member states, special treatment for Least Developed Member States, and that it allows regional economic groups, which consist of only OIC Member States, to participate in TPS-OIC trade negotiations with a unified representation.
3- What is the scope of the preferential system envisaged by the Framework Agreement ?
The preferential system outlined in the Agreement covers all commodity groups, including agricultural products. It extends its limits, besides tariffs, to para-tariff and non-tariff barriers. The preferential system would be revised and further developed in time depending on the needs and in the light of experience gained.
4- What is the difference between signing and ratifying the Framework Agreement ?
Signing is the first step for a Member State in the way of adopting the Agreement. An official of a Member State, specifically authorized for signing the Agreement, could sign the Agreement, the original copy of which is placed at the OIC General Secretariat, Jeddah. It could be signed either in Jeddah or during the annual meetings of the COMCEC.
The second step is the ratification process, which is more complex and time- consuming compared to the first step and depends on the internal procedure of each Member State for ratification, such as approval by the parliament, by the cabinet etc. The ratifying Member State is to send its instrument of ratification,
i.e. the document proving the ratification to the General Secretariat of the OIC.
5- What is the TNC ?
Following the entry into force of the Framework Agreement, the COMCEC established the Trade Negotiating Committee (TNC) in 2003. The main function of the TNC is to embark on negotiations for achieving the objectives of the Framework Agreement, i.e. operating the trade preferential system among its members.
6- What kind of institutional structure do the TPS-OIC trade negotiations maintain ?
The COMCEC is the supervisory body for the implementation of the Framework Agreement, which equips it with the final decision-making power in this regard. It is responsible, inter alia, for establishing the TNC and constituting the TNC’s internal rules, adopting the outcome of the negotiations, and launching rounds of trade negotiations. The TNC, on behalf of the COMCEC, works on implementing the objectives of the Agreement and reports to the COMCEC.
The TNC completed the first round by holding four meetings devoted to designing a tariff reduction modality, between April 2004 and April 2005. Moreover, the second round of trade negotiations for establishing the TPS-OIC was conducted between November 2006 and September 2007.
7- What is the PRETAS ?
At the end of the first round, the TNC agreed on the PRETAS. The PRETAS mainly deals with reducing the tariffs of products covered under the scheme as well as para-tariff and non-tariff barriers. It, furthermore, addresses provisions regarding the future dealings of the TNC.
Following the tenth ratification, the PRETAS entered into force in February
2010.
Tariff reduction part of the PRETAS consists of normal and fast track reductions. Shortly, normal track approach exposes 7% of total HS lines to tariff reduction leading to maximum tariff slabs between 25% and 10%, in 4 years (6 years in the case of LDCs).
Fast track, which is voluntary, has a much broader product coverage between 85% and 70% (LDCs 70%) for tariff reduction, which is to be attained by increasing the margin of preference by 50% on current MFN applied rate at HS level of National Tariff Codes, in 5 instalments (7 instalments for LDCs). Furthermore, the LDCs would access the said marginal preferences from the developing countries in 3 instalments instead of 5.
As for the para-tariff and non-tariff barriers, they will be eliminated upon entry into force of the PRETAS (in the case of the LDCs in 3 years).
8- What is the Rules of Origin ?
The Rules of Origin lays down the rules for determining the origin of products eligible for preferential concessions under the Framework Agreement and PRETAS.
9- When will TPS-OIC become operational ?
The Framework Agreement and PRETAS have already entered into force. TPS-OIC will become operational on the thirtieth day following the receipt
by the OIC General Secretariat of the instrument of ratification of the TPS- OIC Rules of Origin of the tenth Member State. In addition, the Member States that have signed and ratified the TPS-OIC agreements should fulfill their obligations arising from the provisions of these agreements in order to ensure the effective implementation of the TPS-OIC.
10- Which countries have signed/ratified the TPS-OIC Agreements and submitted concession lists ?
Member States that signed / ratified the TPS - OIC Agreement TPS-OIC AGREEMENTS
(As of November 2016)
1- Qu’est-ce que le SPC-OCI ?
Le SPC-OCI est l’un des projets du COMCEC. L’objectif du SPC-OCI est de promouvoir le commerce intra-OCI par l’échange de préférences commerciales entre les Etats membres.
2. Qu’est-ce que l’Accord-cadre sur le SPC-OCI ?
L’Accord-cadre sur le SPC-OCI est le document légal de base du SPC-OCI, qui définit les principes généraux de l’établissement d’un système préféren- tiel, tels que les règles générales des négociations, la portée de la couverture de biens etc. L’Accord est entré en vigueur en automne 2002, après sa ratifica- tion par 10 Etats membres de l’OCI.
Parmi les principales caractéristiques de l’Accord figure le principe de la Na- tion la Plus Favorisée, l’égalité de traitement pour les Etats membres, le traite- ment spécial des Etats membres les moins avancés. Par ailleurs, il permet aux groupes économiques régionaux, comprenant uniquement les Etats membres de l’OCI, de participer aux négociations commerciales du SPC-OCI, dans le cadre d’une représentation unifiée.
3. Quelle est la portée du système préférentiel envisagé par l’Accord-cadre ?
Le système préférentiel décrit dans l’Accord couvre tous les groupes de produits, y compris les produits agricoles. Outre les barrières tarifaires, l’ac- cord s’étend aux barrières para-tarifaires et non-tarifaires. Le système préfé- rentiel serait révisé et développé davantage à l’avenir, à la lumière des besoins et de l’expérience acquise.
4. Quelle est la différence entre la signature et la ratification de l’Accord- cadre ?
La signature est le premier pas pour un pays en voie d’adoption de l’Accord. Un fonctionnaire d’un pays membre, habilité spécifiquement à signer l’Accord, peut signer l’Accord dont une copie originale est préservée au Se- crétariat Général de l’OCI à Djeddah. L’Accord peut aussi être signé à Djed- dah et au cours des réunions annuelles du COMCEC.
La deuxième étape est celle du processus de ratification, plus complexe, consommant plus de temps que la première étape et dépendant de la procédure interne de chaque pays relative à la ratification, telle que l’approbation par le Parlement, le Cabinet etc. Le pays qui ratifie l’Accord est tenu d’envoyer son document de ratification, à savoir le document prouvant la ratification, au Secrétariat Général de l’OCI.
5. Qu’est-ce que le CNC ?
Suite à l’entrée en vigueur de l’Accord-cadre, le COMCEC a créé le Comité de Négociations Commerciales (CNC) en 2003. Les membres du CNC sont les Etats membres de l’OCI qui ont signé et ratifié l’Accord-cadre. La fonction principale du CNC est d’entreprendre des négociations pour réaliser les objectifs de l’Accord-cadre, c’est-à-dire un système opératoire de préférences commerciales entre ses membres.
6- Quelle est la structure institutionnelle des négociations commerciales du SPC-OCI ?
Le COMCEC est l’organe de surveillance pour la mise en oeuvre de l’Accord-cadre qui l’investit du pouvoir de décision finale à cet égard. Il est responsable, entre autres, de l’établissement du CNC et de l’élaboration des règles internes du CNC, de l’adoption des résultats des négociations et du lancement des cycles de négociations commerciales. Le CNC agit pour le compte du COMCEC pour la mise en oeuvre des objectifs de l’Accord et en fait rapport au COMCEC.
Le CNC a achevé le premier cycle en tenant, entre avril 2004 et avril 2005, quatre réunions consacrées à la conception d’une modalité de réduction tarifaire. Par ailleurs, le deuxième cycle des négociations commerciales pour la création du SPC- OCI a commencé en novembre 2006 jusqu’en septembre 2007.
7- Qu’est-ce que le PRETAS ?
A la fin du premier cycle de négociations, le CNC a approuvé le PRETAS. Le PRETAS concerne essentiellement la réduction tarifaire des produits couverts par le Schéma ainsi que les barrières para-tarifaires et non-tarifaires. Par ailleurs, il prévoit certaines dispositions concernant les futures négociations du CNC.
Suite à la dizième ratification, le PRETAS est entré en vigueur en février 2010.
La réduction tarifaire prévue par le PRETAS comprend un processus normal et un processus volontaire accéléré. En résumé, selon le programme de réduction normale 7% des lignes totales SH seront soumises à une réduction tarifaire aboutissant à des tarifs maximum entre 25% et 10% sur une période de 4 ans (6 ans dans le cas des PMA). Ledit 7% des lignes totales HS comprendra uniquement des lignes SH avec un tarif supérieur à 10%.
La réduction accélérée, qui est volontaire, comprend une réduction tarifaire concernant un plus grand nombre de produits, entre 85% et 70% (70% pour les PMA), et qui doit être achevée en augmentant la marge de préférence de 50% sur le taux courant NPF appliqué au niveau SH des Codes Nationaux Tarifaires, sur une période de 5 acomptes (7 pour les PMA). De plus, les PMA pourront bénéficier desdites marges préférentielles de la part des pays en développement, dans une durée de 3 acomptes au lieu de 5.
Quant aux barrières para-tarifaires et non-tarifaires, elles seront éliminées avec l’entrée en vigueur du PRETAS (3 ans dans le cas des PMA).
8- Quelle sont les Règles d’origine ?
Les Règles d’origine déterminent les règles indiquant l’origine des produits éligibles pour les concessions préférentielles sous l’accord cadre et le PRETAS.
9- Quand le SPC-OCI deviendra-t-il opérationnel ?
L’Accord Cadre et le PRETAS sont déjà entrés en vigeur.
Le SPC-OCI deviendra opérationnel trente jours après la réception de l’instrument de ratification des Règles d’origine du SPC-OCI du dixième Etat membre par le Secrétariat Général. De plus, les Etats Membres qui ont signé et ratifié les accords du PSC-OCI doivent remplir leurs obligations stipulées dans les provisions de ces accords en vue d’assurer une mise en oeuvre efficace du SPC-OCI.
10- Quels sont les pays qui ont signé/ratifié les Accords du SPC-OCI et soumis les listes des concessions ?
Etats Membres qui ont signé/ratifié les Accords du SPC - OCI
(Jusqu’à novembre 2016)
1. ما هو نظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي ؟
نظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي هو أحد المشروعات التابعة للجنة الدائمة للتعاون الاقتصادي والتجاري لمنظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي )كومسيك(، ويستهدف تعزيز التجارة البينية فيما بين البلدان الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي من خلال تبادل الأفضليات التجارية فيما بينها.
2- ما هي اتفاقية الإطار الخاصة نظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي ؟
تمثل اتفاقيةُ الإطار الخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي الوثيقةَ القانونية الأساسية لنظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول لأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي، وهي تحدد المبادئ العامة لإرساء ذلك النظام، مثل القواعد العامة للمفاوضات ونطاق السلع المشمولة، الخ. وقد دخلت الاتفاقية حيز النفاذ في خريف عام 2112 ، بعد أن صادقت عليها عشر دول من الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي.
ومن بين الجوانب الرئيسية للاتفاقية مبدأ الدولة الأولى بالرعاية، المعاملة المتساوية للدول الأعضاء، والمعاملة الخاصة لأقل الدول الأعضاء نمو ا ، وسماحها للتجمعات الاقتصادية الإقليمية، التي تقتصر على الدول الأعضاء في منظمة لمؤتمر الإسلامي، بالمشاركة في المفاوضات التجارية الخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية بتمثيل موحد.
3- ما هو نطاق النظام التفضيلي الذي ترتئيه اتفاقية الإطار؟
يشمل النظام التفضيلي الذي تشير إليه الاتفاقية كافة السلع، بما فيها المنتجات الزراعية، فضلا عن الحواجز الجمركية، وشبه الجمركية، وغير الجمركية. ويخضع نظام لأفضليات لمراجعة دورية وتقييم مستمر بغية توسيعه وتطوير أحكامه على ضوء الاحتياجات المطلوبة، والنتائج المستخلصة.
4- ما هو الفرق بين التوقيع على اتفاقية الإطار والمصادقة عليها؟
تمثل عملية التوقيع على الاتفاقية الخطوة الأولى التي تتخذها أي دولة من الدول الأعضاء نحو اعتماد الاتفاقية، حيث يقوم ممثل مخول عن البلد العضو بالتوقيع على الاتفاقية لتي ودع نسختها الأصلية لدى الأمانة العامة لمنظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي في جدة. ويتم التوقيع على الاتفاقية إما في جدة، أو خلال انعقاد الدورات السنوية للكومسيك.
5- ما هي لجنة المفاوضات التجارية؟
بعد دخول اتفاقية الإطار حيز النفاذ، قامت الكومسيك بتشكيل لجنة المفاوضات التجارية في عام 2113 . وتتمثل مهمة اللجنة الأساسية في إجراء المفاوضات الرامية إلى تحقيق هداف اتفاقية الإطار، والتي تتمثل في إرساء نظام فاعل للأفضليات التجارية بين أعضائها.
6- ما هو الهيكل المؤسسي للمفاوضات التجارية الخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي؟
تتولى الكومسيك الإشراف على تنفيذ اتفاقية الإطار، وهكذا تصبح الجهة صاحبة القرار النهائي في هذا الصدد. ومن المسئوليات التي تضطلع بها الكومسيك في هذا المضمار: شكيل لجنة المفاوضات التجارية، ووضع القواعد الداخلية لها، واعتماد النتائج التي تتوصل إليها المفاوضات، وبدء جولات جديدة للمفاوضات التجارية، وذلك ضمن جملة أمور خرى. وتنوب لجنة المفاوضات التجارية عن الكومسيك في العمل على تحقيق أهداف الاتفاقية، وترفع تقارير بهذا الشأن إلى الكومسيك. اختتمت لجنة المفاوضات التجارية ولتها لأولى بعقد أربعة اجتماعات خُصصت لوضع آلية لخفض التعريفة، وذلك في الفترة ما بين إبريل/نيسان 2114 ، وإبريل/نيسان 2115 . كما انعقدت الجولة الثانية من لمفاوضات التجارية لإنشاء نظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة التعاون الإسلامي في الفترة ما بين نوفمبر/تشرين الثاني 2116 ، و نوفمبر/تشرين لثاني 2117.
7- ما هو بروتوكول خطة التعريفة التفضيلية الخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي (بريتاس) ؟
في ختام الجولة الأولى من المفاوضات، وافقت لجنة المفاوضات التجارية على بروتوكول خطة التعريفة التفضيلية الخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في نظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي )بريتاس( الذي يُعنى أساس ا بخفض التعريفات المطبقة على المنتجات المشمولة في الخطة، وكذلك الحد من الحواجز شبه الجمركية وغير الجمركية. ا يضم البروتوكول كذلك على بعض الأحكام التي تتعلق بالأعمال المستقبلية للجنة المفاوضات التجارية. وبعد مصادقة الدولة العاشرة على الوثيقة، دخلت البريتاس حيز النفاذ في براير/شباط 2111 .
8- ما هي قواعد المنشأ ؟
قواعد المنشأ هي التي ترسي القواعد الخاصة بتحديد منشأ المنتجات المؤهلة للحصول على امتيازات تفضيلية بموجب اتفاقية الإطار، وكذا بروتوكول خطة التعريفة التفضيلية لخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية )بريتاس(.
9- متى سيدخل نظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي حيز النفاذ ؟
دخلت حيز التنفيذ اتفاقية الإطار بشأن نظام الأفضليات التجارية بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي و البريتاس سيتم تفعيل نظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي بعد ثلاثين يوما من استلام الأمانة العامة لمنظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي وثيقة مصادقة الدولة العاشرة من الدول الأعضاء في المنظمة لى قواعد المنشأ الخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي. وعلى الدول الأعضاء التي وقَّعت على الاتفاقيات الخاصة بنظام لأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي وصادقت عليها استيفاء التزاماتها التي تقع عليها بموجب نصوص هذه الاتفاقيات، حتى يتحقق تنفيذ ظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي على نحو فاعل. وبعد التوقيع، تبدأ عملية المصادقة، وهي خطوة أكثر تعقيد ا وتستغرق زمن ا طول من خطوة التوقيع الأولى، حيث تعتمد على الإجراء الداخلي المتبع في كل بلد من البلاد الأعضاء، من موافقة البرلمان، ومجلس الوزراء، الخ. وترسل الدولة العضو، التي قامت بالمصادقة على الاتفاقية، وثيقة مصادقتها، أي الوثيقة التي تثبت أنها صادقت على اتفاقية الإطار، إلى الأمانة العامة لمنظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي.
10- ما هي الدول التي وقَّعت/صادقت على الاتفاقية الخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي؟
قائمة الدول التي وقعت أو صادقت على الاتفاقيات الخاصة بنظام الأفضليات التجارية فيما بين الدول الأعضاء في منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي،
